原型模式
克隆羊问题
现有一只羊tom,姓名为:tom,年龄为:1,颜色为:白色。请编写程序创建和tom羊属性完全相同的10只羊。
传统解决方式
1 | package prototype; |
1 | package prototype; |
- 优点:好理解,易操作
- 缺点:创建新的对象时,总是需要重新获取原始对象的属性,如果创建的对象比较复杂时,效率比较低
- 总是需要重新初始化对象,不是动态获得对象运行时的状态,不够灵活
改进思路: Java 中Object类是所有类的根类,Object 类提供了一个clone0方法,该方法可以将一个Java对象复制一份, 但是需要实现clone的Java类必须要实现一个接口Cloneable,该接口表示该类能够复制且具有复制的能力=>原型模式。
原型模式类图
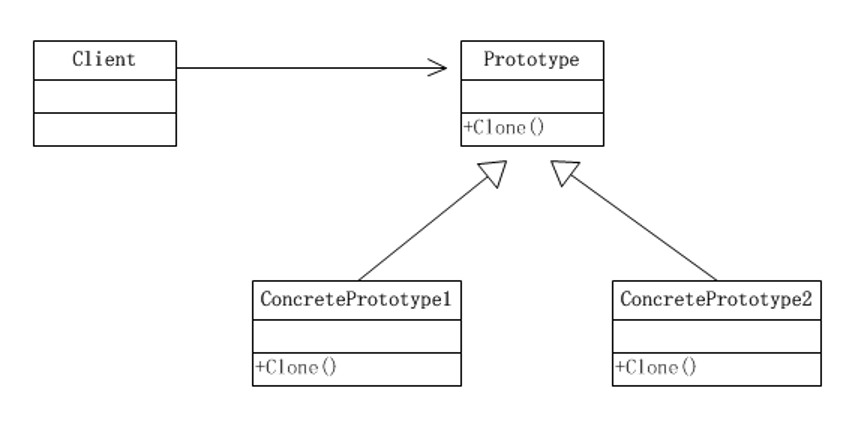
- Prototype:原型类,声明一-个克隆自己的接口
- ConcretePrototype:具体的原型类,实现一一个克隆自己的操作
- Client:让一个原型对象克隆自己,从而创建一个新的对象(属性一样)
原型模式解决克隆羊问题
1 | package prototypeimprove; |
1 | package prototypeimprove; |
浅拷贝和深拷贝
浅拷贝
- 对于数据类型是基本数据类型的成员变量,浅拷贝会直接进行值传递,也就是将该属性值复制一份给新的对象。
- 对于数据类型是引用数据类型的成员变量,比如说成员变量是某个数组、某个类的对象等,那么浅拷贝会进行引用传递,也就是只是将该成员变量的引用值(内存地址)复制一份给新的对象。因为实际,上两个对象的该成员变量都指向同一个实例。在这种情况下,在一个对象中修改该成员变量会影响到另一个对象的该成员变量值。
- 前面克隆羊是浅拷贝。
- 浅拷贝是使用默认的Clone()方法来实现
1 | package prototypeimprove; |
1 | package prototypeimprove; |
运行结果:
1 | sheep1 = Sheep{name='tom', age=1, color='白色', friend=Sheep{name='Jack', age=2, color='黑色', friend=null}} sheep1.friend= 1956725890 |
深拷贝
- 复制对象的所有基本数据类型的成员变量值
- 为所有引用数据类型的成员变量申请存储空间,并复制每个引用数据类型成员变 量所引用的对象,直到该对象可达的所有对象。也就是说,对象进行深拷贝要对 整个对象进行拷贝
- 深拷贝实现方式1:重写clone方法来实现深拷贝
- 深拷贝实现方式2:通过对象序列化实现深拷贝(推荐)
1 | package DeepPrototype; |
1 | package DeepPrototype; |
1 | package DeepPrototype; |
结果如下:
1 | p.name = 2333 p.deepCloneableTarget.hashCode() = 1956725890 |
原型模式的注意事项和细节
- 创建新的对象比较复杂时,可以利用原型模式简化对象的创建过程,同时也能够提 高效率
- 不用重新初始化对象,而是动态地获得对象运行时的状态
- 如果原始对象发生变化(增加或者减少属性),其它克隆对象的也会发生相应的变化, 无需修改代码。
- 在实现深克隆的时候可能需要比较复杂的代码。
- 缺点:需要为每一个类配备一个克隆方法,这对全新的类来说不是很难,但对已有 的类进行改造时,需要修改其源代码,违背了ocp原则,这点请注意。